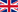
The chaga mushroom is very popular in folk medicine and has been known since the XVI century. It is used both internally and externally in treating various diseases.
The chaga mushroom is very popular in folk medicine and has been known since the XVI century. It is used both internally and externally in treating various diseases.
The versatile medicinal properties of birch chaga owe to its complex and unusual chemical composition. Chaga contains large amounts of nutrients and compounds, the complex combination of which offers the most amazing curative effects, found only in the birch chaga.
Chaga contains substances that, when combined, result in its unique therapeutic properties. In this regard, researchers on chaga have drawn the unanimous conclusion that the main active principle of fungus is a chromogenic polyphenolic carboxylic complex, which has the highest biological activity and is a powerful biogenic stimulant. This complex is unique, and is not encountered in any other fungus of the Hymenochaetaceae family.
Incidentally, it is namely this complex that is responsible for chaga’s rich brown colour and any of the products made thereof. Therefore, we should first of all pay attention to the colour of this fungus – you should not use pieces of chaga that are too light in colour as a medication, as they are certainly much less beneficial than those that are dark and brightly coloured.
On the beneficial elements of birch Chaga mushroom
The birch chaga mushroom (Inonotus obliquus) contains the following:
- 6-8% polysaccharides;
- Up to 60% agaricinic and humic chagic acids;
- 0.5-1.3% organic acids (oxalic acid, acetic acid, formic acid, vanillic acid, purple acid, p-hydroxybenzoic acid, inotodiol and trametenolic acids);
- Pterins (pteridine derivatives), which are caused by the chaga's cytostatic effect;
- Lipids (diglycerides and triglycerides);
- Sterols, in particular, ergosterol;
- Lignin;
- Tetracyclic triterpenes – lanosterol and inotodiol, which exhibit antiblastic activity;
- Fibre;
- Flavonoids;
- Ash (12.3%) that is rich in manganese, which activates enzymes;
- Trace elements of copper, barium, zinc, iron, silicon, aluminium, calcium, magnesium, potassium, and sodium.
Any medicines based on chaga are powerful biogenic stimulators. This should be kept in mind and one should treat chaga with a certain amount of caution. Before taking medicines with chaga, you should always consult with your doctor!
In addition, you should recall that, under high temperatures, most of the chaga’s useful properties are lost. Thus, if you are using chaga as a biogenic stimulant, then, in no case should you boil it, nor should you ever brew it with boiling water! Remember that 90-95°C is the maximum allowable temperature for chaga medications. However, there are some cases, where it is necessary to pour boiling water over chaga or even prepare broth from it. This is done when you wish to completely remove other nutrients contained in this fungus.
So exactly what is chaga capable of? Surprisingly, a lot! Clinical trials have confirmed that chaga has the following benefits:
- Has an antispasmodic, diuretic, antimicrobial action;
- Normalises the gastrointestinal tract and intestinal microflora;
- Promotes the healing of ulcers in the stomach and duodenum;
- Regulates the cardiovascular and respiratory systems;
- Normalises arterial and venous pressure, as well as the heart rate;
- Stimulates haematopoiesis;
- Restores the body's central nervous and neuro-humoral systems;
- Improves metabolism, including the activation of metabolism within brain tissue;
- Increases the body's defences, and the body's resistance to infectious diseases;
- Has anti-inflammatory properties when applied topically and locally;
- Has anti-inflammatory, healing and analgesic effects when used externally;
- Has anti-fungal and anti-viral properties;
- Reinforces the cytostatic activity of anticancer drugs;
- Restores the body's resistance and its defence mechanisms to combat malignancies;
- Reduces blood sugar levels.
During the course of treatment with chaga, it is recommended that you eat the following:
- Vegetable and dairy-based soups,
- Vegetables and fruits,
- Milk, kefir, yogurt, and cottage cheese,
- Pasta and cereals,
- Bread with bran,
- Egg dishes,
- Compotes and jellies,
- Fruit and vegetable juices,
- Mineral water,
- Teas with fruit and herbal supplements.
It should be possible to limit the following things in your diet:
- Animal fats,
- Concentrated broths,
- Sausages and smoked meats,
- Pickles and marinades,
- Hot sauces and spices,
- Dishes that are too hot or too cold,
- Strong tea and coffee.